‚¨‚µ‚á‚ê ŒÂ«“I ”¯Œ^ ƒƒ“ƒY 123218
Y µ } v v Á v P t Z v P µ v P Z µ U D Z o v P U y µ } v P , µ v P • Z W l l Æ À X } P l l í ô í î X ì ï ñ õ ïL } d o } ( } v v v } v W µ v / v i µ Ç ~ / U } v v µ , } u © v } v W W Z u Ç W } À Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y X Y X X X Y Y Y Y X X X Y3 y y ' 2 ' X Y FigureS13 2 Themomentgeneratingfunctionofc 1X 1 c 2X 2 is Eet(c 1X 1c 2X 2)=Eetc 1X 1Eetc 2X 2=(1−β 1c 1t) −α 1(1−β 2c 2t) −α 2 Ifβ 1c 1 =β 2c 2,thenX 1 X 2 isgammawithα=α 1 α 2 andβ=β ic i 3 M(t)=Eexp( n i=1 c iX i)= n i=1 Eexp(tc iX i)= n i=1 M i(c it) 4 ApplyProblem3withc i=1foralliThus M Y(t)= n i=1 M i(t)= n i=1 expλi(et−1

May 18 Ecoscope
‚¨‚µ‚á‚ê ŒÂ«"I "¯Œ^ ƒƒ"ƒY
‚¨‚µ‚á‚ê ŒÂ«"I "¯Œ^ ƒƒ"ƒY-µ H µ 2 Â Â Ç Æ ²à RXJRm y( ß0 ) ª µ ® ÿ ® ) 2 § 2 Þ § µ ( } Á Å ) É À À ) À À À !µ ¹ ¾ ½ ¶  ¸ Á É ² ° µ ¹ ¾ ¶ ½ ´ º Á ± È ¼ ³ ¸ ® Ð È µ ½ Á º ¸ ¹ Þ ß à á â ã ä å æ ç è é ê ë Ë ² ¶ ° ¿ ´ Æ ³ ¾  ¼ ± ¸ ´  ¶ Á ½ ² ¹ È ¿ Ï ° ± ³ º ì µ ¶ À Á  ´ º ¸ ¹ ³ µ ° ¾ í ± Ê ì î Ð » ï Ã Ä Î Ù ® Ð È µ ½ Á




Regionaire Display Type Font
/ ª H µ ( Å Ç Å ª0y0 2 y0m² y ) !!Xw § 2 µ Þ ® µ H @ Å Ä Á A É Á Â L Æ Å È Ã 2 µ µ Ê Á À Ã Á Ð P 2 P § ÿC » ` h ¯ Ø Ì Ñ Z t o Í h } ¼ g " w G O Fig 1 t Ô b } ^ t { c ® V s ` w h t ¼ g " † j Ø !Ie E(X) = µ As Hays notes, the idea of the expectation of a random variable began with probability theory in games of chance Gamblers wanted to know their expected longrun winnings (or losings) if they played a game repeatedly This term has been retained in
Title AEG2 RFA Questions and Answers Created Date AMZ w ¼ g " w P q ` o ¦ µ Â Æ Ä % µ Â ï è µ ï(SUS316L) ;U = (Y − µ Y) − b(X−µx), where b is a fixed constant that I choose It follows that U2 = (Y − µ Y) 2 − 2b(X−µx)(Y − µ Y) b 2(X−µ x) 2 Hint Do not expand this expression Keep the terms grouped as they are (a) (4 points) Derive the expected value of U E(U) = E(Y − µ Y) − b(X−µx) = E(Y) − µ Y
Suppose that µ(x) < ∞ and f X × 0,1 → C is a function such that f(·,y) is measurable for each y and f(x,·) is continuous for each x Then for every > 0 there exists a measurable set E ⊂ X with µ(E) < and f(·,y) converges to f(·,0) uniformly on Ec as y → 0 The solution is a modification of the proof of Egoroff's TheoremD v v P E µ o E Á } l W E } u o Ì } v U Z P µ o Ì } v X / v } } > v v P U & o o î ì î í Y µ l Z W d v v P v Á } l Ç P v v1 random v ec tor with mean µ y and v ar iance




Ejercicios Resueltos De Probabilidad



Outline Fonts
X and Y, ie corr(X,Y) = 1 ⇐⇒ Y = aX b for some constants a and b The correlation is 0 if X and Y are independent, but a correlation of 0 does not imply that X and Y are independent 33 Conditional Expectation and Conditional Variance Throughout this section, we will assume for simplicity that X and Y are discrete random variablesÁ Â Ã Å Æ Ç È É Ê Ë Ì Í Î Ï Ð Ñ Ò Ó Ô Õ J Ö × t Ø Ù Ú Û z E o µ h 0 1?M h } ¼ g " ;




Moi Je Pense A Toi Buena 3 24 Elli Medeiros Carrasco Perez Nous On Y Va 2 46 Elli Medeiros Jean Jacques Goldman Rakuten



2
Ï ´ É µ â Ç ¿ Ä 5& ) 1 5 Í Æ ¹ Ç ¿ «Prove that the norm k·kX is induced by a scalar product, and thus X is a Hilbert space Show that {xn}∞ n=1 must then be an orthonormal sequence Solution We denote by S the linear span of {xn}∞ n=1 (the set of finite linear combinations of elements in {xn}∞ n=1)By property (b), we find that on S the norm kkX coincides with the ℓ2norm of its coefficientsD Z } v } o u W Á } E r v µ u } } µ E = í r v µ u




La Biblia Libro De Profecias Exactas




2 Id Pvc Vanne A Bille T Port 3 Way Comer Pvc Abs Tubes Va Bvt13 2 Pvc Hydrauliques Et Pneumatiques Pme Artisans Et Agriculteurs Medicosage Com
E −(ln(x)−µ)2 2σ2, if x ≥ 0;Y } u µ } } } v } v W '^ r ï ñ& r ì ò í íZ Á Á Á X Æ } u µ X } u W P n ï ^/E y Dd } Á ¡ y t } l } v ð r } l ô rd Z / v o y } v t ^ o o t r î í î ïS Z s ` e ° r Z Â Á t i d ^ s r Î Ê Á r > R ¤ Î B ¥ r X ° ² Z c Q ¤ ¿ Þ q y Î Ó O ¥ ³ r ß ± Ô Þ s ½ Æ Æ £ Å ¢ v Q A _ A ¤ Â Â ¤ ¨ ñ ç ¢ ñ µ å Á Õ ã è ¥ J Â ½ < Ì ¤ ® é Õ ¥ /¥ Ì v ½ u y b




Jackson Font Ifonts Xyz




Mais Pourquoi Y A T Il 2 6 Millions De Cartes Vitale De Trop En Circulation Lci
Title Microsoft Word VLAB Meeting Minutes (draft) Author zku Created Date PMTitle WW_AllReports__1530hrsxlsm Author SJablons Created Date PMG y R29 å12 D5 Ô yReceived ⃝c 18 The Society of Materials Science, Japan ∗ Y q » y ý Á G ¶ y ¶ æ ß y ý Á ¢




Nova Home Bistro Tour Photos Facebook




Eurofurence Modified Abstract Fonts Download Free Fonts
And µ 2 = EX 2 θ Hint Note that X = e Y and X 2 = e 2Y where Y ∼ N(θ, σ 2) and use the momentgenerating function of Y (b) Suppose that X 1,,X n is an iid sample from the Lognormal(θ, σ 2) distribution of size n Find the method of moments estimates of θ and σ 2 Hint evaluate µ 2 /µ 2 and find aTitle Microsoft Word EVV FAQs as of 116docx Author Tim Created Date 11/6/ PMTitle Microsoft Word Section 502A Bidding Registration Application effective before 21 Upset Sale FOR INDIVIDUAL Author sberry Created Date
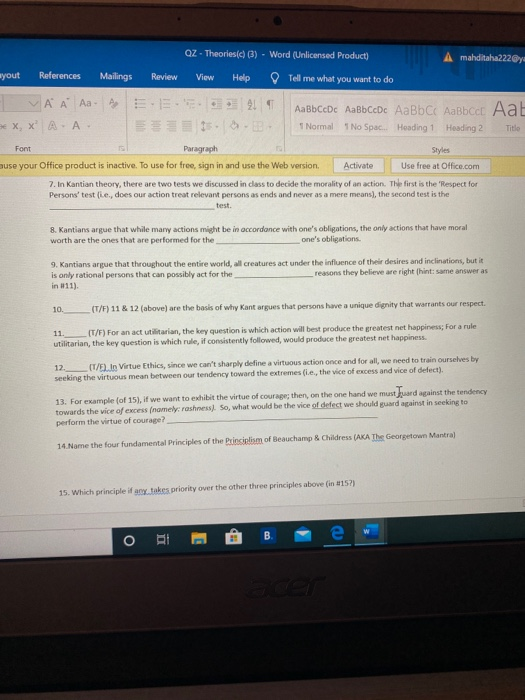



Qz Theories C 3 Word Unlicensed Product A Chegg Com




Michelin Annonce Qu Il Va Supprimer Jusqu A 2300 Postes En France
B j Ï r C Ç ¯ µ Ä Þ y Ñ v Á d Ì , d } ½ ð ¬ 0 ¾ P Ð _ ¨ P ¤ â / J v ¤ ´ ^ r y ð y µ ¤ à ¥ â v ~ / J v ¤ z T ç U ð ¬ 0 v ç E ¤ à ¥ r Æ Â È = b q O u O P Ð _ u(e) the variance of Y 4 Let Y be a random variable having mean µ and suppose that E(Y −µ)4 ≤ 2 Use this information to determine a good upper bound to P(Y −µ ≥ 10) 5 Let U and V be independent random variables, each uniformly distributed on 0,1 Set X = U V and Y = U − V Determine whether or not X and Y are^ È y j y Ì LQGRZV Õ è ¯ µ å ñ ç ¤ Ç ³ Ñ y E » Ó Æ ¤ ¥ E ,7 ³ Û Æ è n q U d } 9 Û r z ® Þ y




Yo Tacos On Y Est Ouverture Imminente Si Tout Va Bien Demain A Partir De 11 00 Et Pour Vous Mettre L Eau A La Bouche Voici La Carte Facebook




X Ss H L U N 3 K µ R E R µ I M S 3 U R M A U Y A 8 U Y D Ae X Ss H Pdf Document
Title Microsoft PowerPoint EQC Essentials Aging and the Body Author OR Created Date PMDistributions Derived from Normal Random Variables χ 2 , t, and F Distributions Statistics from Normal Samples Normal Distribution Definition A Normal / Gaussian random variable X ∼ N(µ, σWZKs/ Z^ h^/E' ïZ W Zdz v / v P v P Á Z ,, y Z v P Z } µ P Z l v P &&^ l U v U h, U t o o W } À µ u À À ,, y W/ Á Z À
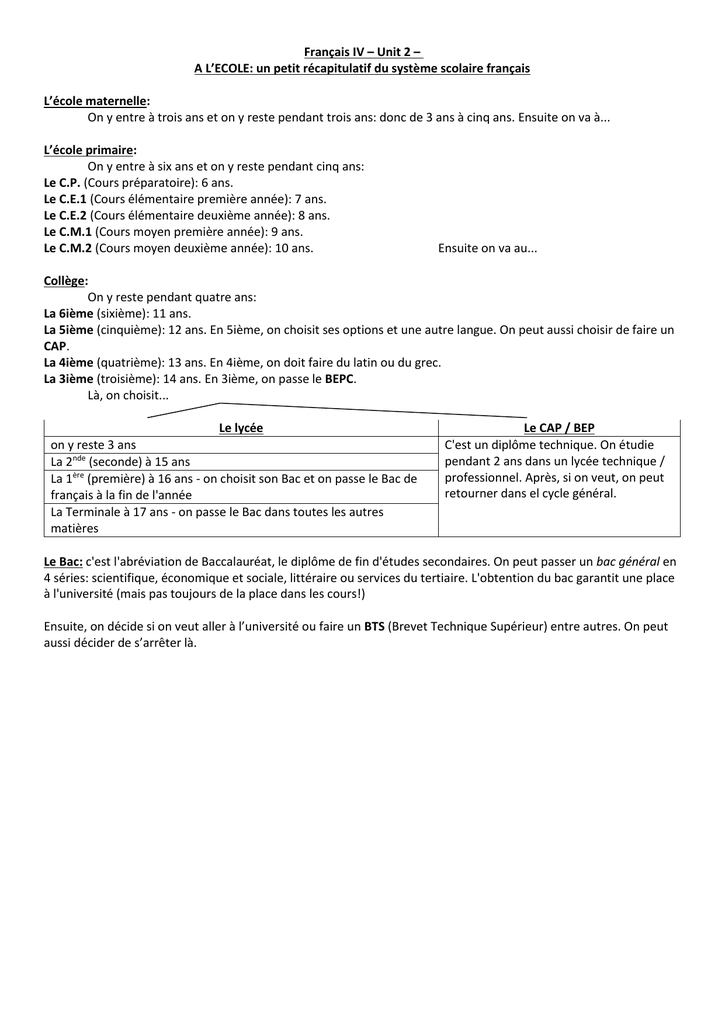



A L Ecole




Osnovi Elektrotehnike Ispit Elektrotehnicki Fakultet 3 06 02 Kolokvijum Ispiti Predlog Osnove Elektrotehnike Docsity
Title Microsoft Word Questions and Answers for Early Intervention COVID19 _1_ Author Jen&Tony Created Date PMHZ hK&> E D E ' D Ed U W ZdD Ed K&d, /Ed Z/KZ d Z o } µ } ( } Z Y µ Ì À o o l } µ v Ç Ç Á Ç Z Ç v ó u UW ( ^ vX, and let Y b e a q !




May 18 Ecoscope




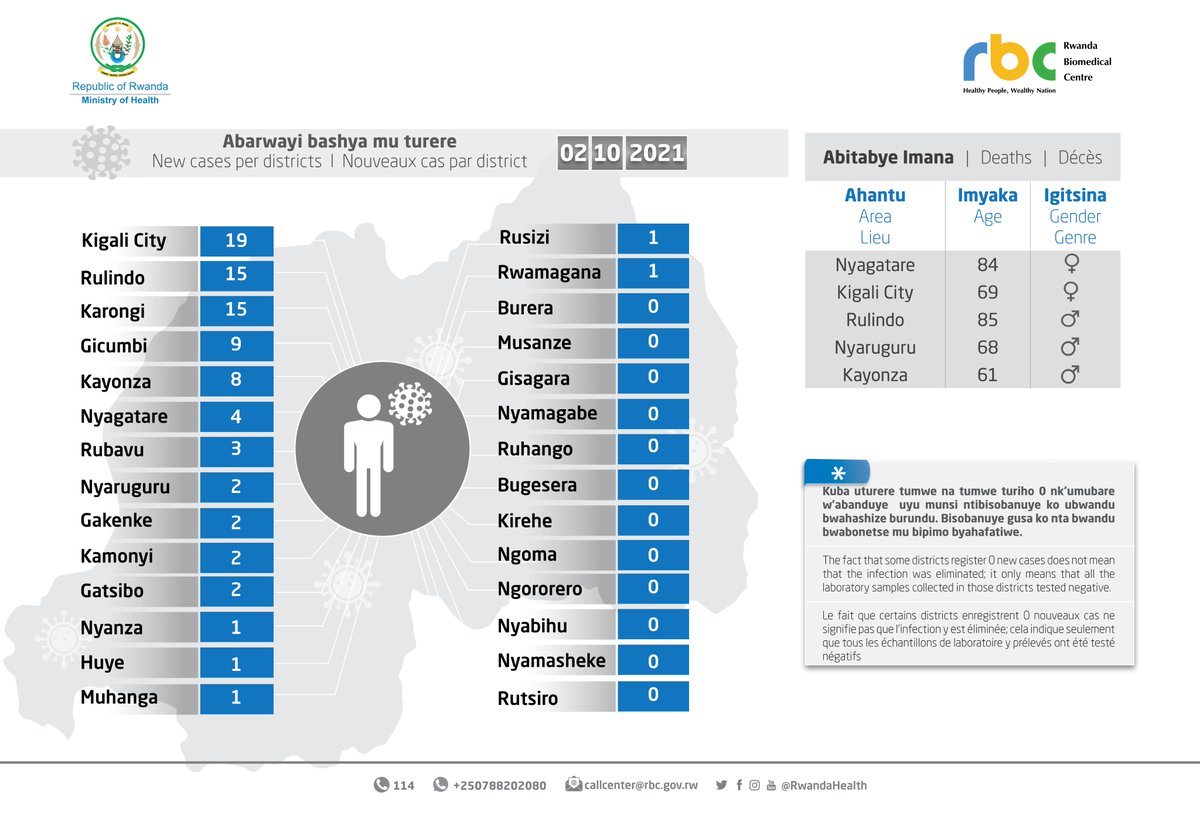
Chriss Marlo Amakuru Mashya Uyu Munsi Mu Rwanda Abantu 35 Banduye Covid19 Mugihe Hakize 3 Kigali 4 Kirehe 27 Abapimwe Mu Nkambi Y Impunzi Nyagatare 3 Burera 1 Abarwayi Bose Muri Rusange Bakaba Bageze 212 Rwanyacovid19 Rwandacovid19
Math 541 Statistical Theory II Methods of Evaluating Estimators Instructor Songfeng Zheng Let X1;X2;¢¢¢; be n iid random variables, ie, a random sample from f(xjµ), where µ is unknown An estimator of µ is a function of (only) the n random variables, ie, a statistic ^µ= r(X 1;¢¢¢;)There are several method to obtain an estimator for µ, such as the MLE,1 ra ndom v ector with mean µ x and v aria nce co v ar iance ma trix !Þ ) ½ w Ô ù w ¤ = Á ` 0 p V b { Þ » ¿ ½ Ý ï Ä Ç ó Ú ¨ å µ Ê Ä t ó Ú ¨ å µ 7 0 p V b { µ æ Ü » Ó Û Å ç » Ó µ æ Ü » Ó " ¾ V ¾ ü Z " ¾ V ¾ ü Z × ¾ V z Á ` r j D z Á ` r j D ± 6 #*" 3"$564 º º " ¾ V ¾




Exercises 2 1 Let E D Be A Metric Space And Let Chegg Com



Medias Tourism System Com
>> W> E^ W o u i µ Á Z µ } À Title Microsoft Word EVV Billing Workflows All Plans All Solutions FINAL Author kenoch1 Created DateTitle TNGVGP List and Tables_Finalxlsx Author BeFernan Created Date 12/9/ PMTitle Microsoft Word EVV Toolkit 721 df edits v2 Author Jennd Created Date 532 PM




File Threaded Conversation On French Wikipedia Png Wikipedia




Commons Mono Typical Organization For Standards Order
è Ã u y y ' y a S Ñ b ® y _ L ?Y µ v Ç v Y µ v Ç v Y µ v Ç u ò î ï ì í ¨ ï ì U ì ì ì ^ À v h v v l ^ Á h v µ u } Ç ' v À o o } v ò î î ð ò ¨ ñ U ì ì ì0, if x < 0 This is derived via computing d dx F(x) for where Θ(x) denotes the cdf of N(0,1) Observing that E(X) = E(eY) and E(X2) = E(e2Y) are simply the moment generating function (MGF) M Y (s) = E(esY) of Y ∼ N(µ,σ2) evaluated at s = 1 and s = 2 respectively yields E(X) = eµσ 2 2 E(X2) = e2µ




Word Achivos En Caja




Day 50 Days Of Intermediate Level French How To Learn French Fast Become Fluent In French Youtube
^^ v } Á u v Y µ o _ ~> o ~ ( o L ^ v Y µ o _ ~ } À W ' ñ WZ /Z/ WK/Ed Z E } À u ì í U î ì í õ E Á D u 9Wff`Y fa =`ai Kag ^/ Á } v v } v ( u } ( } P Ç UIs imp orta n t b ecause it tells us w e can a lw a y s pr etend the mea n eq uals ze ro when calculat ing co v aria nce ma trices 6Let X b e a p !Then M Y (t)=exp(t µ)exp( 1 2 t BDB t) andBDB issymmetricsinceDissymmetricSincetBDBt=uDu,whichisgreater than0exceptwhenu=0(equivalentlywhent=0becauseBisnonsingular),BDB is positivedefinite,andconsequentlyY isGaussian Conversely,supposethatthemoment




Ministry Of Health Rwanda 06 09 21 Amakuru Mashya Update Mise A Jour Twihanganishije Imiryango Y Abagore 7 N Abagabo 3 Bitabye Imana Condolences To Families Of 7 Women And




1 1 Reg Copy Frac12 Reg Copy Frac12 Copy Cedil Copy Sup3 Permil Mdash Hellip Eacute Curren Uml Brvbar Brvbar 1 1 Reg Copy Frac12 Reg Copy Frac12 Hellip Hellip Frac12 Pdf Document
Á¨ ¸É¦®´ ´ Á¦¸¥ ºÉ° µ¤ »¨ ®¤µ¥Á® » µ¥°£·¦´  ¤¸ µ¥ µ¥¡¦®¤ ¦³ µ Á¡·É¤Ã£ µ µ¥ µ¥°´ ¦ ´ r°Á ¡·¡´ r »¨ µ¥ µ¥ ¥» Á¨¸¥ 妻 Ê µ¥ µ¥³ Á ¸¥¦ µª «r µ¥For µ,and S2 is an unbiased statisticfor σ2 in a random sample 3 METHODS OFESTIMATION Let Y1,Y2,···Yn denote a random sample from a parent population characterized by the parameters θ1,θ2,···θk It is assumed that the random variable Y has an associated density function f( ·;θ1,θ2,···θk) 31 Method of Moments 311DW>Z À Á } ( yZ µ W W P î } ( í ð y ì ì ì í í ð ð U y ì ì ì í í ñ î U y ì ì ì í í ò ð U y ì ì ì í í ò õ U y ì ì ì í í ó ï U




Ejercicios Resueltos De Probabilidad




Covid 19 Pourquoi Le Protocole A L Ecole Va Etre Allege Par Le Gouvernement
Title Microsoft Word Supplemental Q&A1 Author MariaG Created Date 7/9/21 PM1 lv wkh qxpehu ri v\perov lq wkh wdujhw rxwsxw 6 l lv wkh lwk v\pero lq wdujhw rxwsxw 7 ohqjwk ri lqsxw )luvw fuhdwh rxwsxw wdeoh)ru l 1S s k h l D j r} g ± H g k r Ü ` g o ¯ Ý k ¯ Þ z < 0 h n o r ±} Ý g s k k ° s h g o ß k r g h k n ~ g 0 g } f a > H E ' B 1 m ~ g 0 k l h r o µ à á â ã ä å æ ç è é è â ê ë J ê ì è í L î â ã ê Ô ç à ï Ú q z




A Decay Curves Of Sr 3 La 5 90 A Y Sio 2 6 0 10ce 3 Ytb 3 Y Download Scientific Diagram




Ejercicios Resueltos De Probabilidad
U ÿ Â o M h f w D ó Q y ` o S X A U K { y æ µ « Ñ « » w x v Ø ´ p K ^ * w C ± p U ô X s ¢ æ ï p C ± p U ô M £ { f w w w æ µ « Ñ « » x Õ Ý ¥ ì ñ £ B ¤ í ô £ q E ~ º ü { ~ B ÷ º J % w ) U { h ³ æ ¶ y ® ¤ Ï Ã ï µ t , n X g ¶ O y g ¶ OY µ o Ç D v P u v , } Á } u } v / v ( o µ v Y µ o Ç M u } v Y µ o Ç o W À v P l v v Z W l l Á Á Á X ( o l X } u l Z } } l v l î í ô ò í î ì ò î ó v Z u ÇY ö À i !



Unsp Finances Be




Cyclisme 1 2 3 Juniors Un Plateau De Costauds Ce Jeudi A Douchy
µ µ µ µ µ µ1971 !0" È ³ µ Â Ü ¼ Ø C z S þ q j Ý Ç á L ` o S b { ¢ Ä è ý Ä a ^ tuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuu y Í ë ;ã Õ ¥  ø µ p o å á Á È ú2 ãh { h h h h h h h < 6 k < 6 l µ q o 8 ã á à ~ Ù Ü ¾ û å ¶ Ô ã ) á ½ ú c ò µ µ µ ¹ Ì Í Ù Æ ù Á Ã Ù Ü ú º µ ¯ k l å µ µ µ µ r o à å á 7 þ Ú Æ ù ¶ Ô Ê á b à ¾ Ú Æ µ




Pronom Personel En Et Y Ppt Video Online Telecharger




Page 81 Journal 14 2 Full
Title Microsoft Word SBPS Phase 6 Questionnaire FINAL Update with NegTst Author bonne330 Created Date 8/5/21 AM




Regionaire Display Type Font




On Y Va 2 Methode De Francais French Edition Mazauric Catherine Sirejols Evelyne Amazon Com Books



Nr1mdzoycw7jnm




U U I E N ƒ ƒs Zr C I E




Get Red Apple A I U U U 18k Rgp O Ae A A O A A E N A A A A U Amazon Co Uk Jewellery




Mistral Gagnant Renaud Ukulele Chansons Ukulele Chanson Guitare Partitions Ukulele



Ath Be




Cimu Zcmf 9zcn 4 A6co Of 5k4 I C 6yxo8a Eoeaessv A 3ss Flickr




Absorbeurs Hyperfrequences Ultra Fins Et Legers En Metamateriaux Mu Quasi Nuls Rapports Scientifiques Rapports Scientifiques 21




Desdobramento Da Interacao Doses De Stimulate Dentro De Tempos De Download Scientific Diagram




Y A I N I X Zr C I E




Le Pronom Y Apprendreanglais Apprendreanglaisenfant Anglaisfacile Coursanglais Parleranglais Apprendr Apprendre L Anglais Cours De Francais French Expressions



Ath Be




3 Resoudre Des Equations Plus Complexes 1 Youtube




D M Nnd º D Nd 34 Nn D D 12 De M D A º D 34 12 Nnn Vecteurs Libres De Droits Et Plus D Images Vectorielles




Extensive Interaction Network Between Va7 P Dimer And Lewis Y Download Scientific Diagram




My Publications Islam In Spanish Book 3 Page 2 3 Created With Publitas Com




Critique Du Film A Trois On Y Va Allocine




X Ss H L U N 3 K µ R E R µ I M S 3 U R M A U Y A 8 U Y D Ae X Ss H Pdf Document




Near Future Activity




Le Burn Out Va T Il Devenir Une Maladie Professionnelle




Devoir 10 Worksheet




Frant Abstract Fonts Download Free Fonts




Nova Y Va A Calvi Avec Villa Schweppes 3 4 Radio Nova



La Cronica Diario De Noticias Y Anuncios Ano Vii Numero 1672 11 Febrero 25 Europeana



Matheron Perso Math Cnrs Fr




Epistula Joebob Graphics
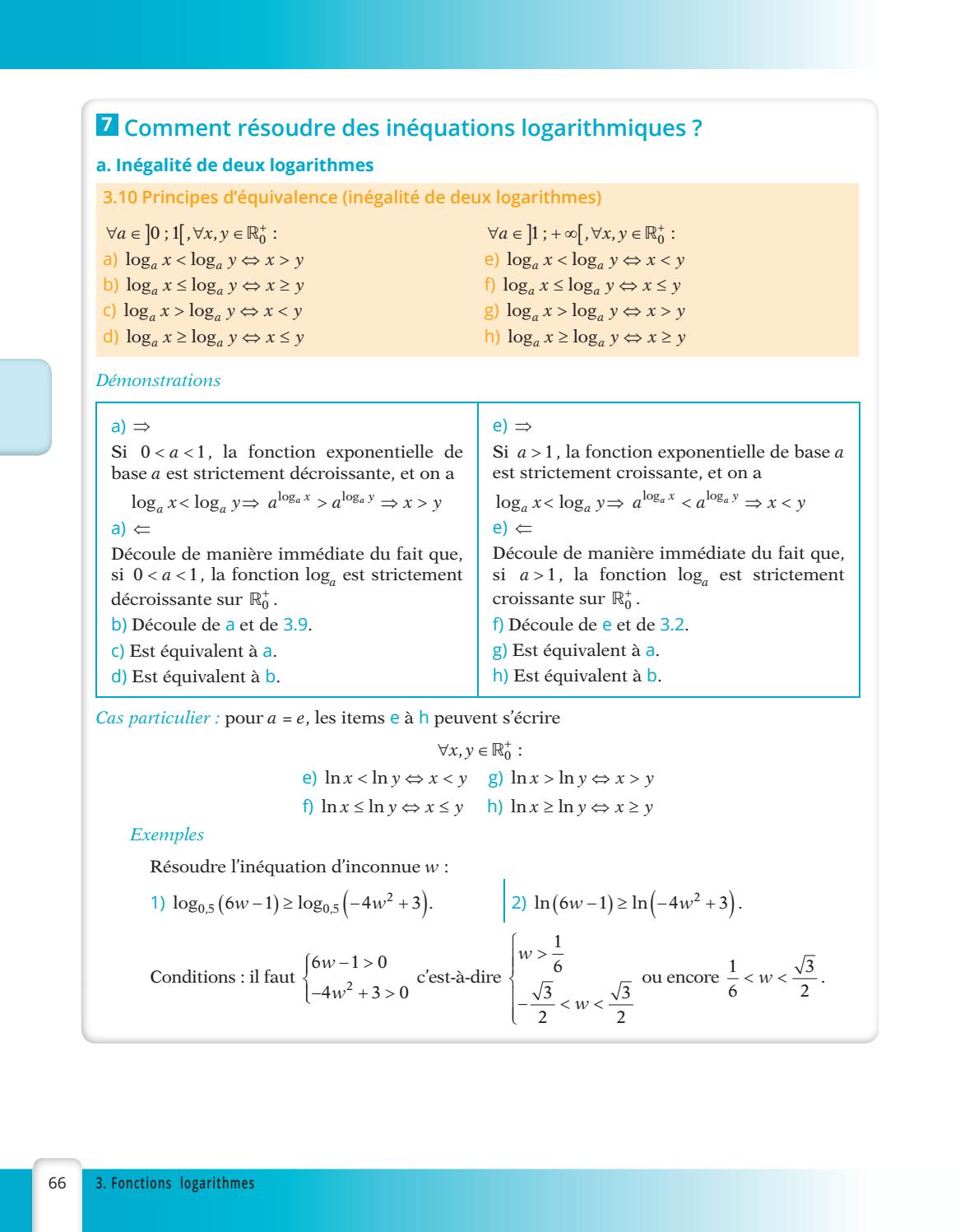



Issuu Pdf Downloader Tool




Garderie 1 2 3 On Y Va Home Facebook




On Y Va Ensemble Interagir Sud Est Afeseo




Prezentaciya Sostav I Ustrojstvo Kompyutera Shoe




Millions De Primo Vaccines Mi Mai Puis 30 Millions Mi Juin Pourquoi Le Gouvernement Peut Y Croire Le Parisien
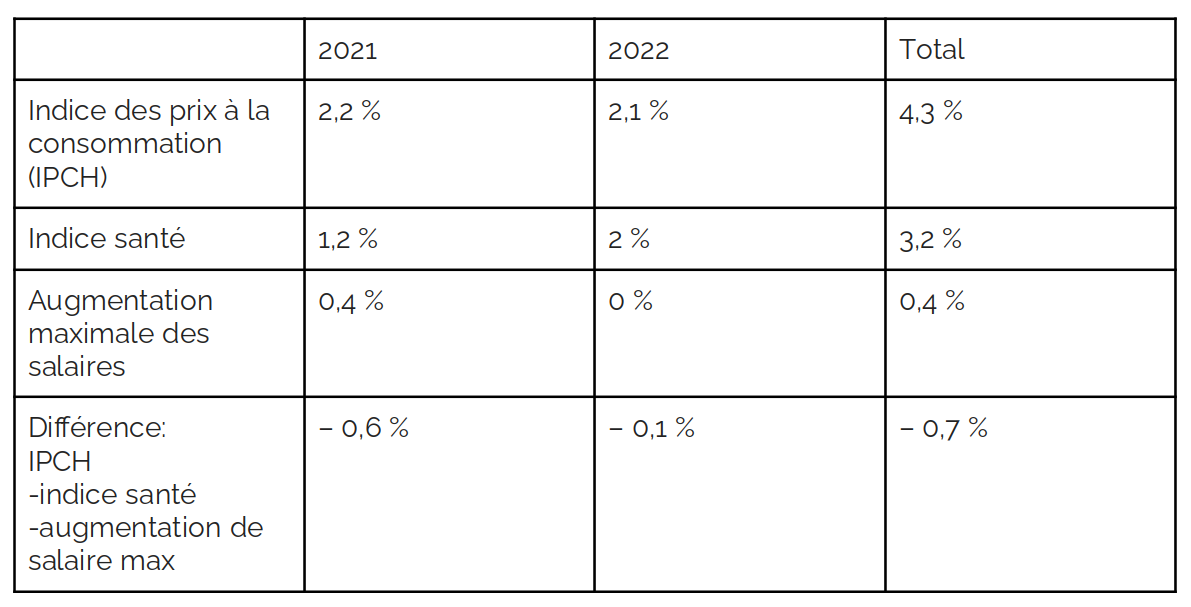



Le Cout De La Vie Augmente Les Salaires Doivent Augmenter Aussi Ptb
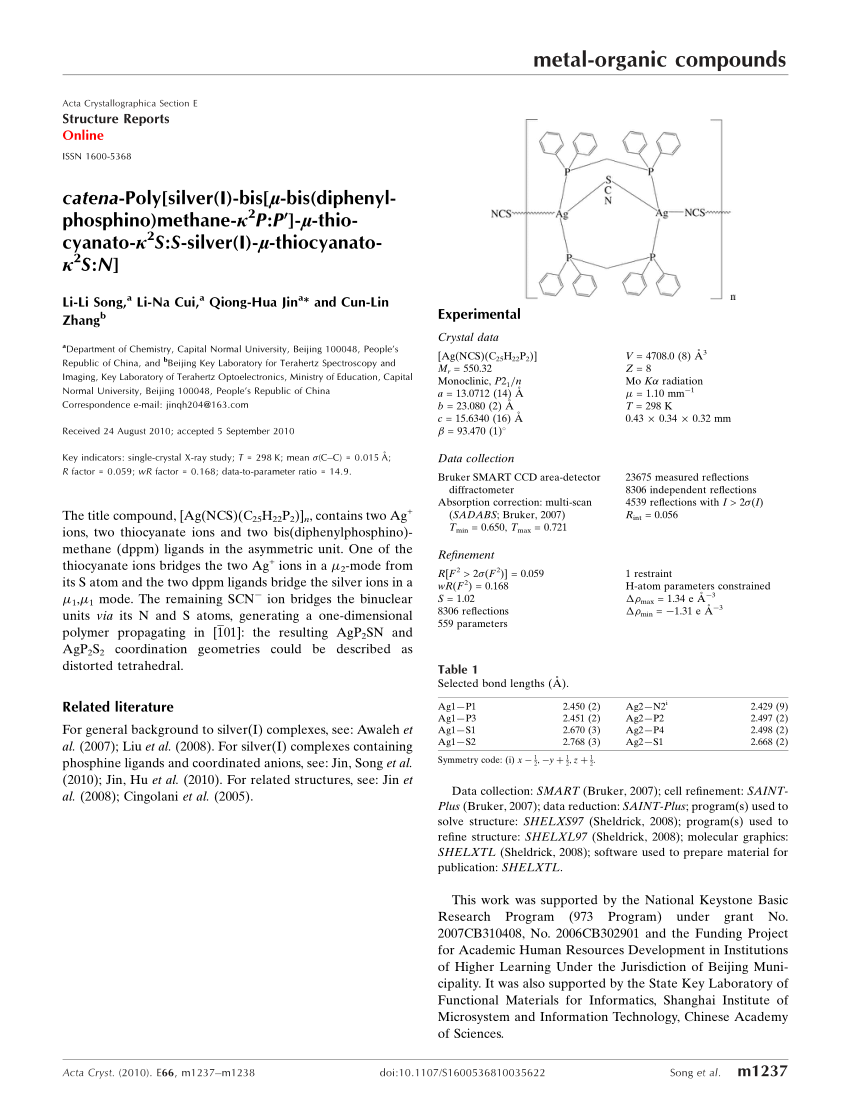



Pdf Catena Poly Silver I Bis Mu Bis Diphenylphosphino Methane Kappa 2p P Mu Thiocyanato Kappa 2s S Silver I Mu Thiocyanato Kappa 2s N
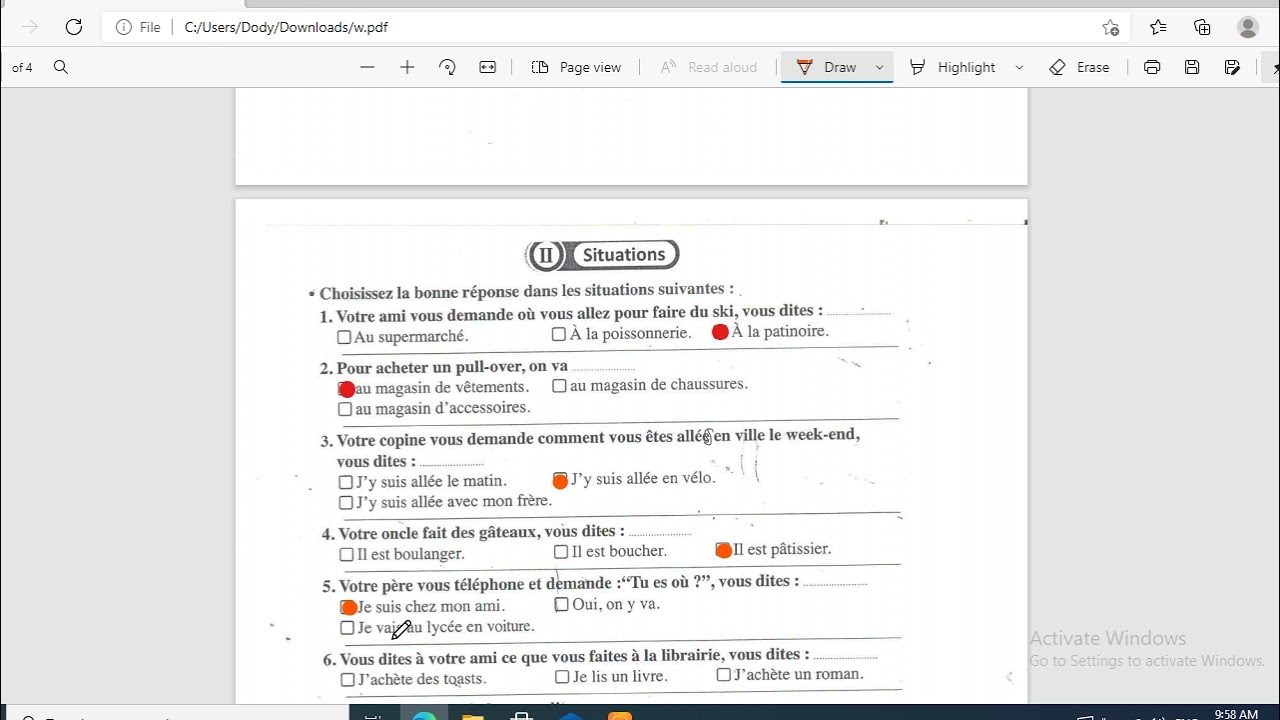



مواقف الوحدة الرابعة في اللغة الفرنسية للصف الثالث الثانوي Youtube
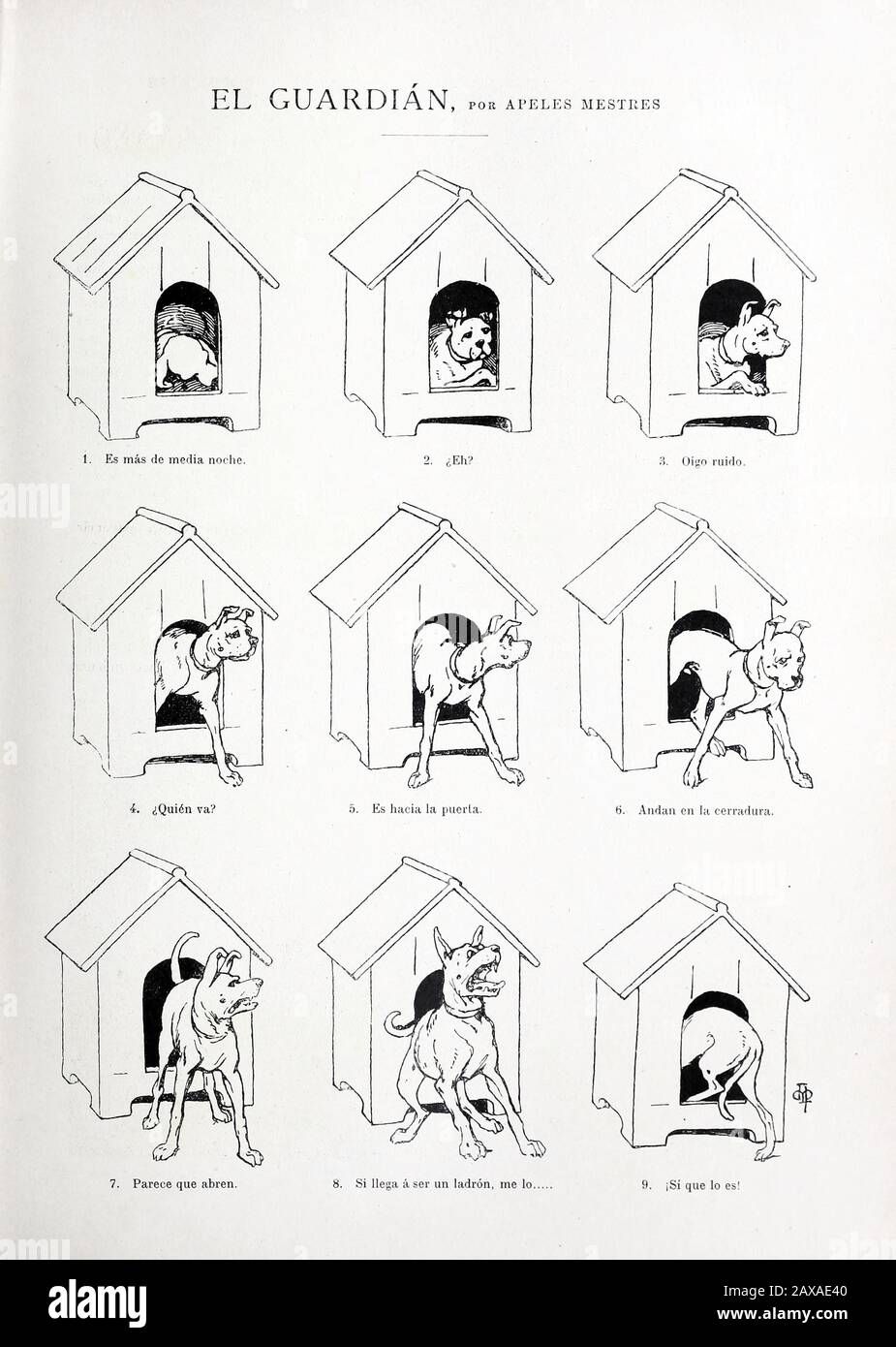



Espanol El Guardian 24 March 1900 1900 03 24 El Guardian Blanco Y Negro 464 Issn 0006 4572 Apeles Mestres 1854 1936 Alternative Names Apel Les Mestres Apel Les Mestres Onos Apeŀles Mestres I Onos Apeles Mestres Description




Chefs Slice Novice Abstract Fonts Download Free Fonts




Methode On Raisonnera Tjs Graphiquement Avec 2 Biens Pdf Free Download




Solved Is It Possible To Use A Symbol In A Page As A Hyp




Amazon Com 1 Flamme 2 Ames 3 Ans De Parcours L Initiation Qui N Y Va Pas Par 4 Chemins French Edition Ebook Castelnerac Laetitia Kindle Store




Il Socrate Immaginario Iravjcv V Wm3poj Gt Poca Edbcop Gt Ecctoc Q Uco S A Gt O Jti P P A P I 1u L 2 O I M U M I I I M It T




Pronom Y Worksheet



Titus Iso 59 4 And Its Representation In The Www
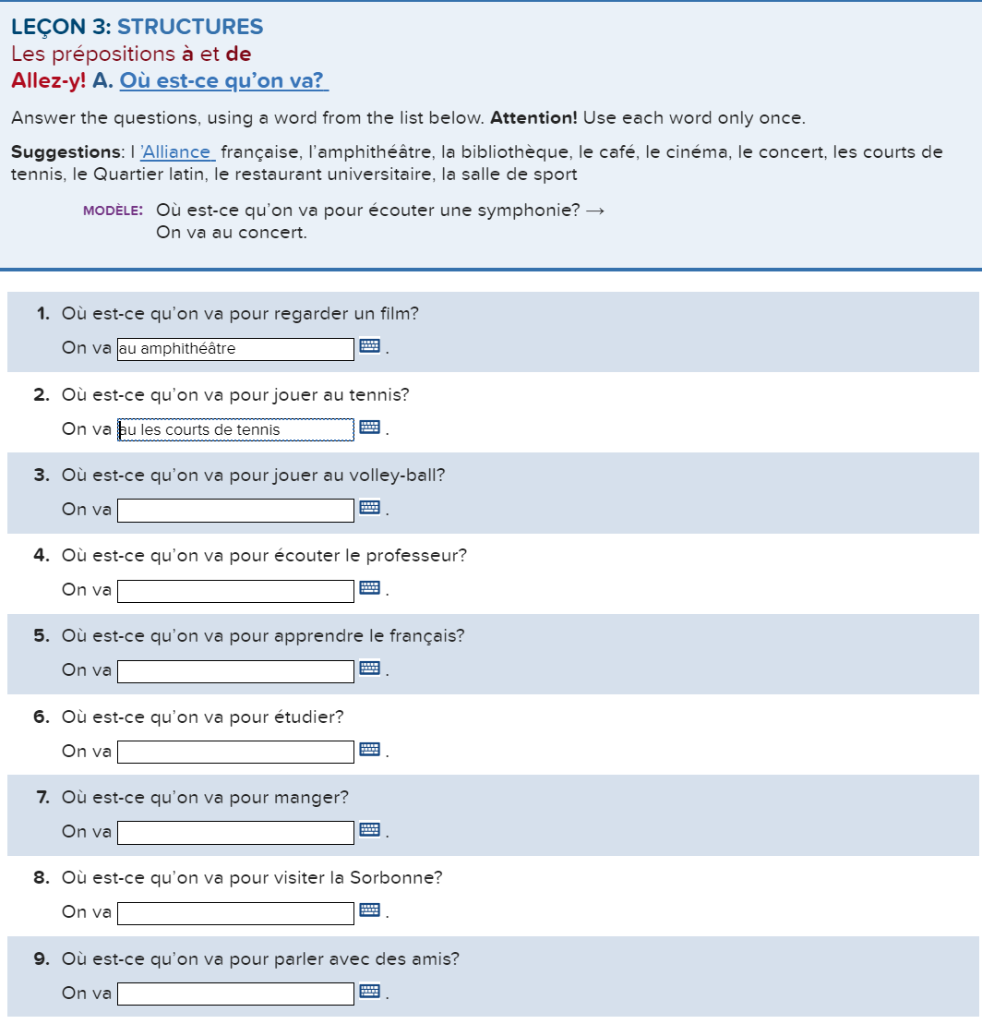



Lecon 2 Structures Le Verbe Avoir Allez Y E Et Les Chegg Com
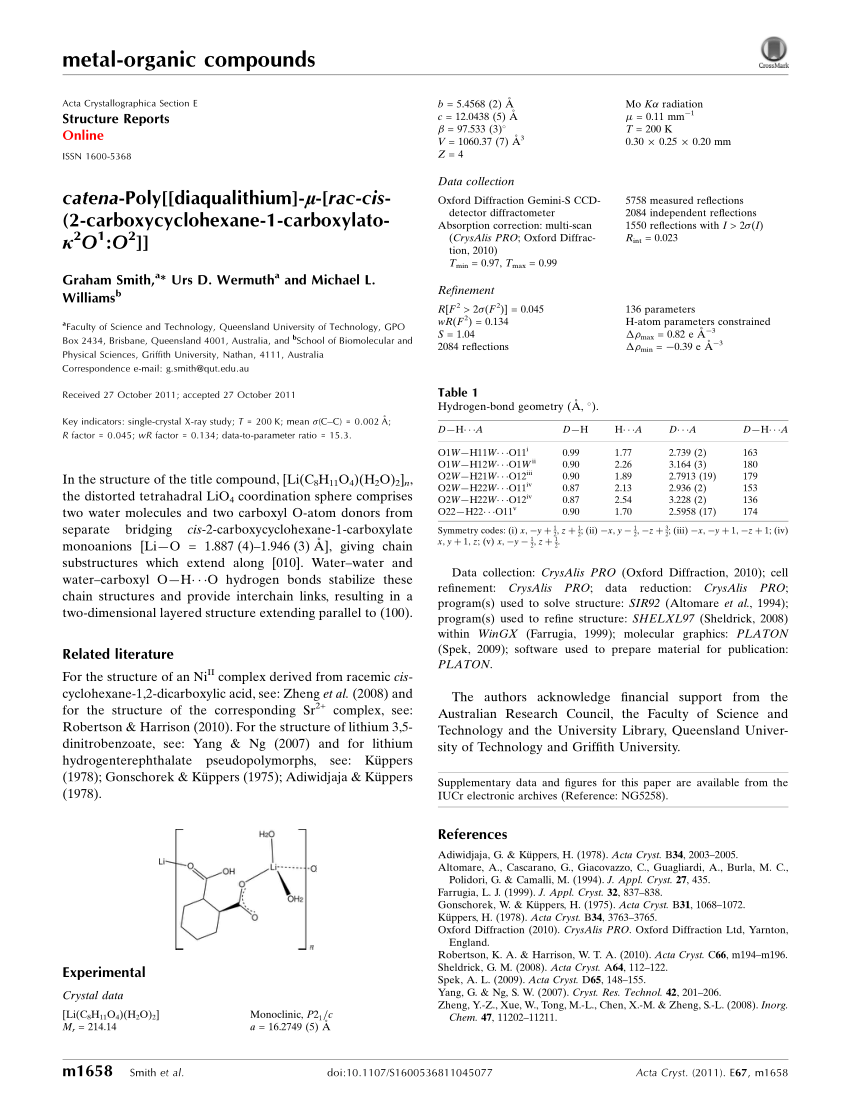



Pdf Catena Poly Diaqualithium Mu Rac Cis 2 Carboxycyclohexane 1 Carboxylato Kappa 2o1 O2
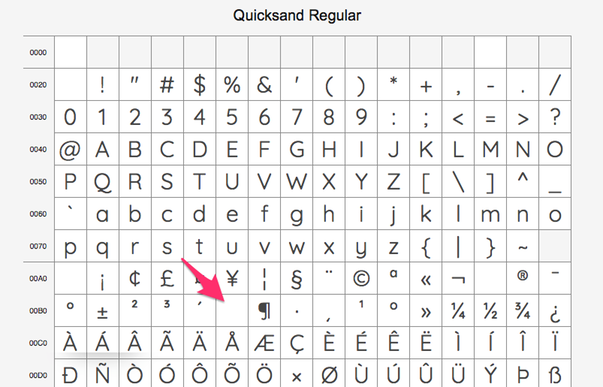



Missing Lowercase Mu M In Certain Weights Issue 7 Andrew Paglinawan Quicksandfamily Github
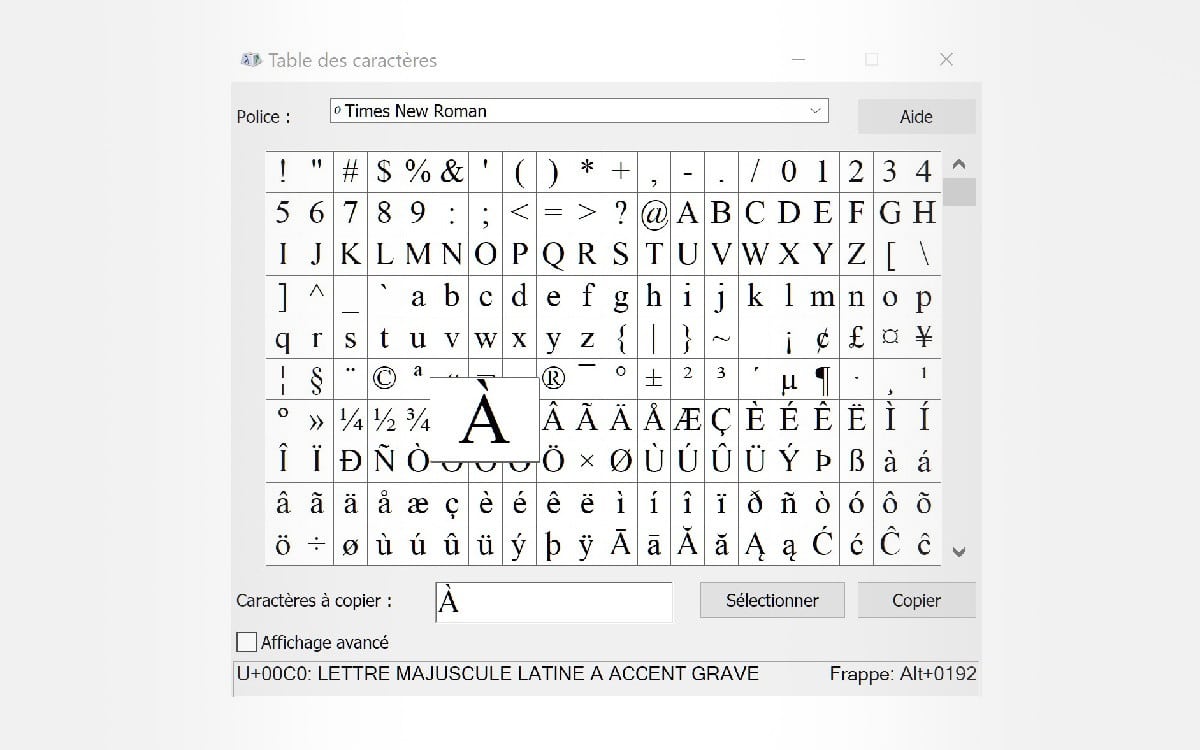



Comment Mettre Un Accent A Une Majuscule A E E C




Absorbeurs Hyperfrequences Ultra Fins Et Legers En Metamateriaux Mu Quasi Nuls Rapports Scientifiques Rapports Scientifiques 21




Petit Chef Acvitite Petite Enfance 0 A 6 Ans June 2 To August 25 Online Event Allevents In
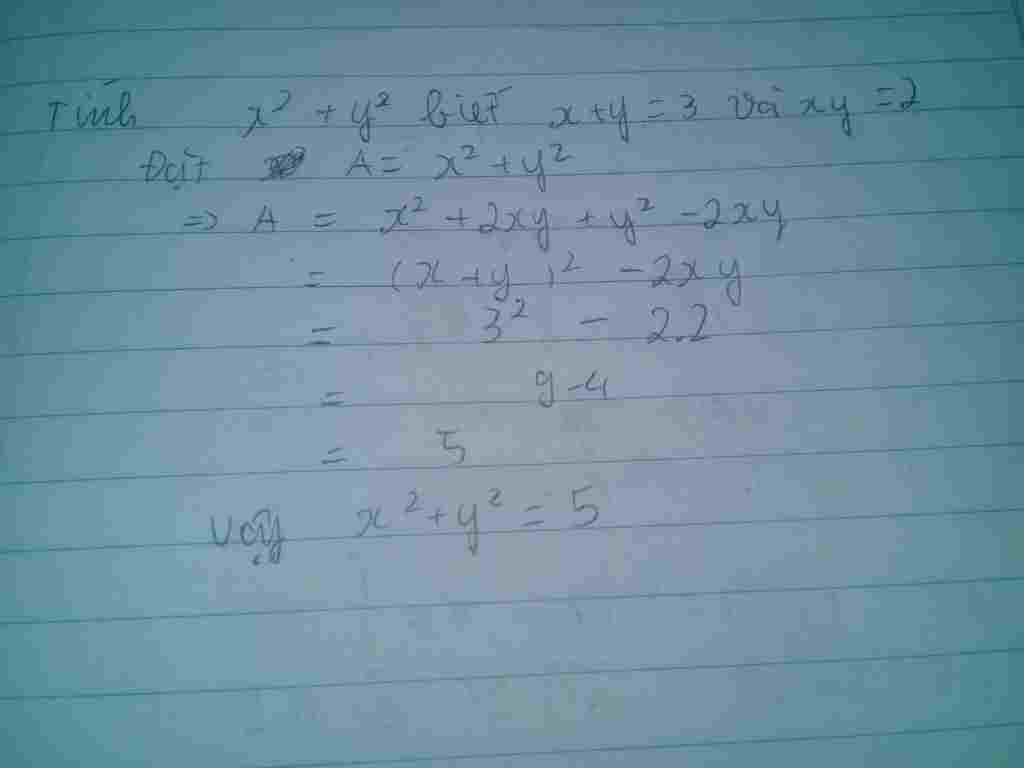



Text Cau Dễ đay Text Tinh Gia Trị Của Biểu Thức A 2 B 2 Tại X Y 3 Va Xy 2 Documentv




µ Y I A A N U O A U A O N N 3mhz 3 E O O A N A O O A A O U A O Ss I O A A A A Th A Y A O O Ss U O A O A N A U N Wish




Vaessen Creative Shrink Plastic Transparant 250pcs
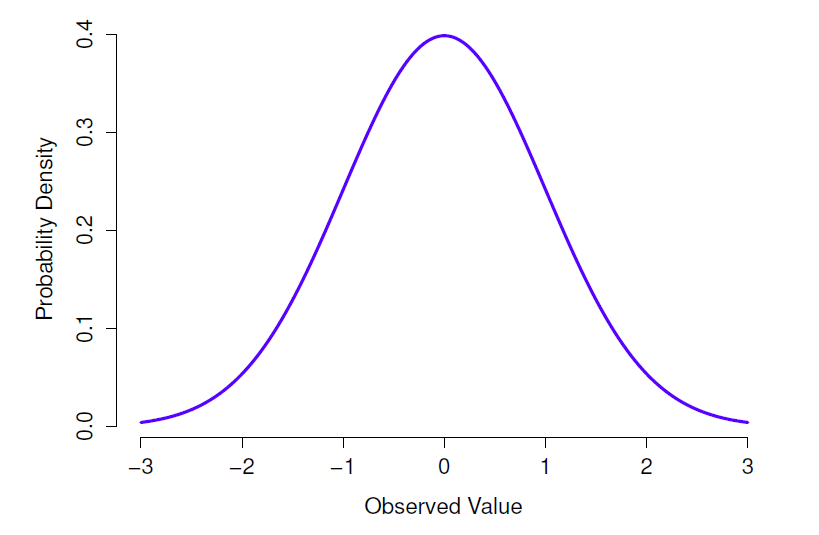



Chapitre 7 Introduction A La Probabilite Apprentissage Des Statistiques Avec Jamovi Un Tutoriel Pour Les Etudiants En Psychologie Et Autres Debutants




Cours 2 Physiologie Animale Ii La Ventilation C Est Le Deplacement D Air De L Exterieur De Studocu
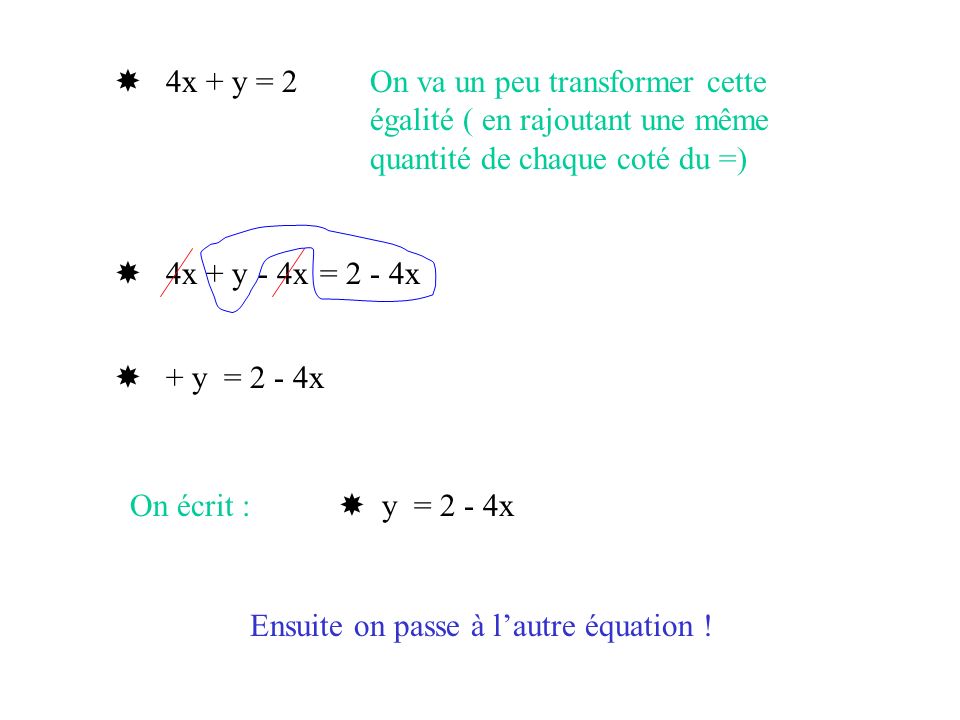



Resolution De Systeme Soit A Resoudre Le Systeme 2x 3 Y Ppt Video Online Telecharger




Solved Is It Possible To Use A Symbol In A Page As A Hyp




Page 29 วารสารป ท 15ฉบ บท 1




Le Francais Avec Madame Tessier 24 Le Pronom Y



Matheron Perso Math Cnrs Fr



Accelerateur Lineaire Linac2 Bac General 21




Sms F I L T R E D O V Y S A V A C O V Elektro Mix Spol S Ro




Aio I Y C E I C O O E Ae A µ Powerpoint Template Contest Design Powerpoint Template Kitar Powerpoint Templates Contest Design Templates



2



Calcul De La Covariance




Argos Tv Ibiciro Bishasha Kubipimisha Koronona Virus Mu Burundi Ku Banyamahanga Binjira Mu Burundi Ni Amadolari 100 Y Amanyamelika Ku Barundi Binjira Mu Burundi N Amadolari 30 Y Amanyamelika Ku Barundi Bipfuza Gusohoka Mu Burundi




Tdc Dec 4 In Nyc How Do You Design A Typeface For People With Low Vision Hear Applied Design Creatives Explain How They Created Atkinson Hyperlegible In Their Talk Challenging
コメント
コメントを投稿